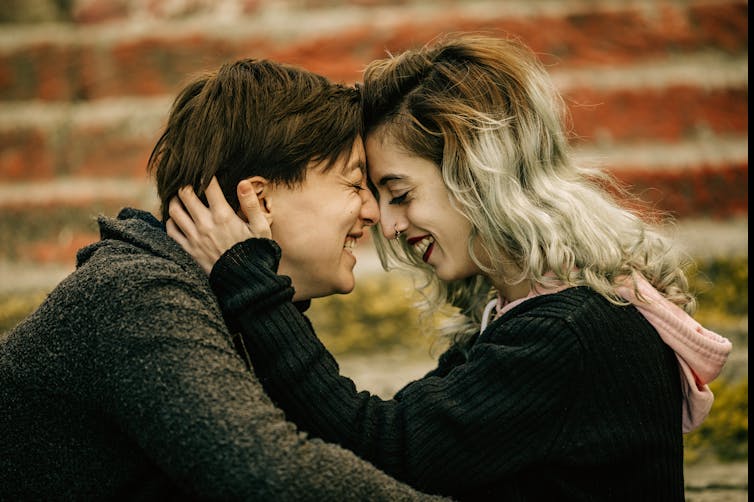
Most adults identify themselves as heterosexual, meaning they report being attracted to, and engaging in sex with, only members of the other sex.
Sean G. Massey, Binghamton University, State University of New York; Mei-Hsiu Chen, Binghamton University, State University of New York, and Sarah Young, Binghamton University, State University of New York
However, women ages 18 to 29 are increasingly rejecting exclusive heterosexuality and describing their sexual orientation in other ways. These changes in women’s sexuality are not mirrored by their male peers.
That’s the primary finding in our most recent report on nine years of surveys at the Binghamton Human Sexualities Research Lab, just published in “Sexuality in Emerging Adulthood.” Together with our Binghamton University colleagues Richard E. Mattson, Melissa Hardesty, Ann Merriwether and Maggie M. Parker, we conclude that changes in young adults’ sexual orientation are not just a result of increased social acceptance of LGBT people – but also are related to feminism and the women’s movement.
LGBT progress
These findings align with recent polling by the Gallup Organization, which found that American adults are increasingly identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender or more than one of those. The Gallup report attributed these changes to increasing public awareness and acceptance of people who identify as LGBT, as well as the influence of a 2015 U.S. Supreme Court case legalizing same-sex marriage nationwide. Another potential factor was proposed federal legislation banning discrimination on the basis of gender identity or sexual orientation.
But our study goes beyond those poll results, showing that young American adults are shifting away from heterosexuality in how they identify themselves when asked about their identities and how they describe whom they are attracted to and with whom they have sex. That indicates something more is happening than an increasing willingness to “come out” and identify as LGBT.
The fact that these differences are larger among women than men indicates, we believe, that feminism and the women’s movement have, in fact, begun to change female sex and gender roles.
Compulsory heterosexuality
In the early 1980s, lesbian feminist Adrienne Rich argued that what she called “compulsory heterosexuality” was the primary cause of gender inequality. She said that because social pressures and threats of violence – as well as actual violence – force heterosexuality on women, that made women dependent on and subservient to men in all areas of life, including gender roles and sexual expression.
Our research indicates that one outcome of more than a century of feminist activism and progress may be women’s increasing resistance to compulsory heterosexuality and its consequences. As a result, more women under 30 are moving away from exclusive heterosexuality than men in the same age group.
In a related development, we found that women in this age group are also reporting more open attitudes toward sex than previous generations of women. They are separating sex from traditional love relationships, describing themselves as enjoying casual sex with different partners and more likely to have sex with a person before being sure the relationship would become serious or long term. These attitudes are more akin to those of their male peers.
The shift is more pronounced among women who are moving away from exclusive heterosexuality, and less obvious among women who report they are exclusively heterosexual.
There’s much more to learn
We still have a lot of questions about these trends. We wonder how they affect the ways that these young adults engage in sex and relationships. We also don’t know how women who identify themselves as not exclusively heterosexual negotiate and navigate sexual relationships with men – or whether these trends will continue as they age.
We are also interested in why men in this age group are less likely than women to reject exclusive heterosexuality – but are more likely to report exclusive homosexuality. And we’d like to know whether, or at what point, those who are not exclusively heterosexual might come out to family and friends – and if they deal with things like anti-LGBT prejudice.
As human sexuality becomes increasingly diverse, it remains unclear whether the political and social landscape will affirm these changes or threaten those who are expressing that diversity. We are hopeful that the continued success of the LGBT and feminist movements will push society toward an affirming future.
[Over 100,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletter to understand the world. Sign up today.]![]()
Sean G. Massey, Associate Professor of Women, Gender and Sexuality Studies, Binghamton University, State University of New York; Mei-Hsiu Chen, Director of Statistical Consulting Services, Lecturer, Department of Mathematical Sciences, Binghamton University, State University of New York, and Sarah Young, BSW Program Director, Assistant Professor of Social Work, Binghamton University, State University of New York
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.